•
312 Rules (Sequence)
Suppose that 「aₙ」 and 「bₙ」 are convergent sequences with limits A and B respectively; then the following rules apply:
❶ Sum rule
「aₙ+bₙ」 converges to A+B.
❷ Product rule
「aₙ·bₙ」 converges to A·B.
❸ Quotient rule
「aₙ/bₙ」 converges to A/B, provided that ...
9707#3775
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
COMMENT
3775
•
322 Basic null sequences
ᐥThe following are null sequences.
❶ 「1/n˄p」 for p>0
❷ 「c˄n」 for |c|<1
❸ 「n˄p·c˄n」 for p>0 and |c|<1
❹ 「c˄n/n!」 for c∈ℝ
❺ 「n˄p/n!」 for p>0ᐥ
Proof of ❶
∀ε>0 ∃N∈ℕ such that N > 1/ε.
n > N
⇒ n > 1/ε
⇒ 1/n < ε
⇒ |1/n−0| < ε
「1/n」 is a null sequence.
By the p ...
9707#9722
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
9722
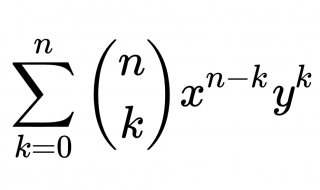 •
322_ Binomial Expansion
•
322_ Binomial Expansion
ᐥ(a+b)˄n
= 「「nꞒk」·a˄(n−k)·b˄k Σk=0,n」
= 「n!/((n−k)!·k!)·a˄(n−k)·b˄k Σk=0,n」ᐥ
(a+b)˄1
= 「1!/((1−k)!·k!)·a˄(1−k)·b˄k Σk=0,1」
= a+b
(a+b)˄2
= 「2!/((2−k)!·k!)·a˄(2−k)·b˄k Σk=0,2」
= a˄2+2·a·b+b˄2
(a+b)˄(n+1)
= (a+b)˄n·(a+b)
= (a+b)˄n·a+(a+b)˄n·b
= 「n!/((n−k ...
9707#9688
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
COMMENT
9688
•
335 Subsequence
ᐥThe sequence 「a⸤n⸤r⸥⸥」 is a subsequence of the sequence 「a⸤n⸥」 if 「n⸤r⸥」 is a strictly increasing sequence of natural numbers.
「a⸤n⸥ Ƚn→∞」 = L ⇒ 「a⸤n⸤r⸥⸥ Ƚn→∞」 = L
「a⸤n⸥ Ƚn→∞」 = ∞ ⇒ 「a⸤n⸤r⸥⸥ Ƚn→∞」 = ∞ᐥ
9707#5220
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
5220
•
343 Cauchy sequence
ᐥA sequence 「aₙ」 is a Cauchy sequence if and only if for every ε>0 there exists a natural number N such that n,m>N ⇒ |a⸤n⸥−a⸤m⸥|<ε.
A sequence is convergent if and only if the sequence is a Cauchy sequence.ᐥ
If 「a⸤n⸥」 is a convergent sequence, then for a ...
9707#5221
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
5221
•
34_ 「(1+1/n)˄n」 is convergent
(1+1/n)˄n
= 「n!/((n−i)!·i!)·1˄(n−i)·(1/n)˄i Σi=0,n」
= 「(1/i!)·n!/(n−i)!·(1/n˄i) Σi=0,n」
= 「(1/i!)·「(n−j) Πj=0,i−1」·(1/n˄i) Σi=0,n」
= 「(1/i!)·「(n−j)/n Πj=0,i−1」 Σi=0,n」
= 「(1/i!)·「(1−j/n) Πj=0,i−1」 Σi=0,n」
< 「(1/i!)·「(1−j/(n+1)) Πj=0,i−1」 Σi=0,n」
< 「(1/i!) ...
9707#9767
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
9767

-


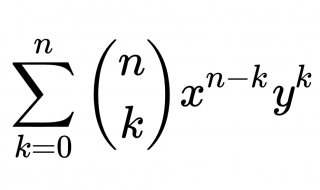 •
322_ Binomial Expansion
•
322_ Binomial Expansion