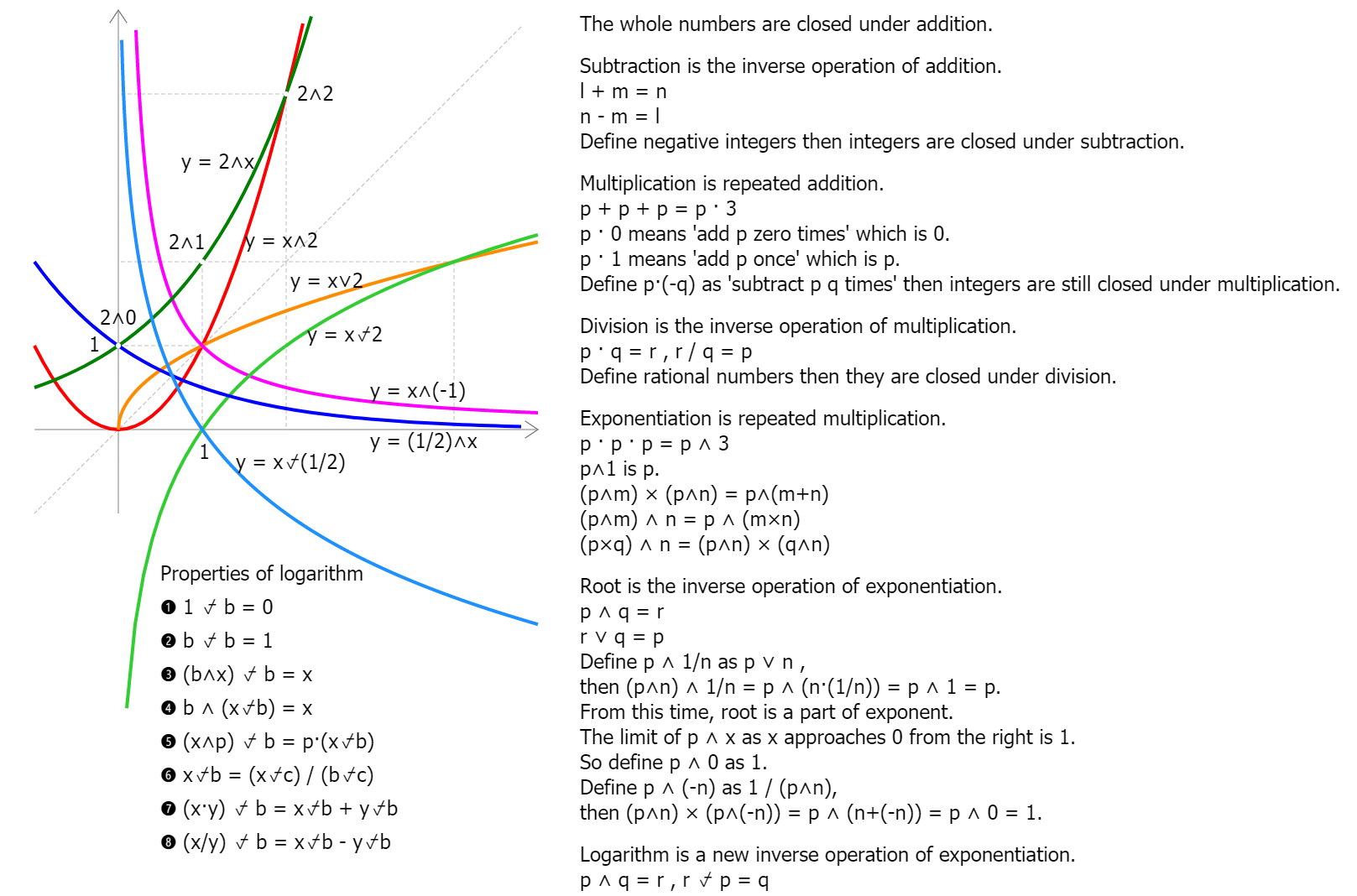
In mathematics, the notion of number has been extended over the centuries to include 0, negative numbers, rational numbers such as 1/2
and −2/3, real numbers such as √2 and π, and complex numbers, which extend the real numbers with √−1.
 •
number
•
number
A number is a count or measurement. It is really an idea in our minds.
○ count: the total determined by counting
○ measurement: the size, length or amount of something, as established by measuring
5148#9577
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
9577
 •
0750± positional notation
•
0750± positional notation
By the 8th century, Indian mathematicians had perfected positional notation and over the next several centuries, Arab merchants, scholars and conquerors began to spread it into Europe.
-- vigesimal, Maghreb, Hebrew, glyph, Aztecs, duodecimal, sexigesimal
5148#4984
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
4984
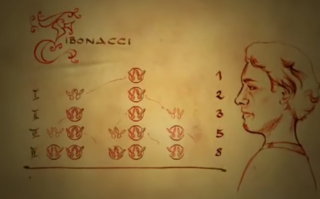 •
1202 Leonardo Fibonacci
•
1202 Leonardo Fibonacci
Fibonacci asked himself how many pairs of rabbits originated from a single pair in one year. Each pair of rabbits will produce exactly one more pair of both sexes per month which in turn would be fertile from the second month after birth.
5148#4759
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
4759
 •
1571 - 1630 Johannes Kepler
•
1571 - 1630 Johannes Kepler
Keplar observed that the relationship between a number in Fibonacci sequence and the previous number more and more closely approaches the irrational number Φ the longer the sequence is continued and Φ describes nothing other than the golden section.
5148#5056
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
5056
 •
1643 - 1727 Isaac Newton
•
1643 - 1727 Isaac Newton
Galileo had already discovered some years prior that the distance traveled by a falling object is represented by a function of time.
Newton wondered how one could calculate the velocity of the object at any particular instance during the fall.
5148#5035
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
5035
 •
BC 0300? Euclid
•
BC 0300? Euclid
It was the Greek mathematician Euclid who produced the first precise description of the golden section.
A length is devided into two parts in such a way that the smaller part is to the larger part in the same proportion as the larger one is to the whole.
5148#5055
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
5055
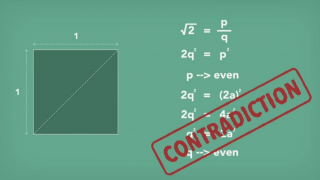 •
BC 0500? Hippasus
•
BC 0500? Hippasus
According to Pythagoras theorem the diagonal length of a square with each side measuring one unit would be square root of two.
The assumption that square root of two could be expressed as a ratio of two integers deduces a contradiction.
5148#5026
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
5026

-

 •
number
•
number
 •
0750± positional notation
•
0750± positional notation
 •
1202 Leonardo Fibonacci
•
1202 Leonardo Fibonacci
 •
1571 - 1630 Johannes Kepler
•
1571 - 1630 Johannes Kepler
 •
1643 - 1727 Isaac Newton
•
1643 - 1727 Isaac Newton
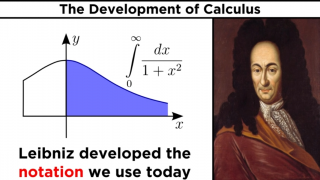 •
1646 - 1716 Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
•
1646 - 1716 Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
 •
1900± Crisis in Mathematics
•
1900± Crisis in Mathematics
 •
BC 0300? Euclid
•
BC 0300? Euclid
 •
BC 0500? Hippasus
•
BC 0500? Hippasus
 •
BC 0570 - 0495 Pythagoras
•
BC 0570 - 0495 Pythagoras
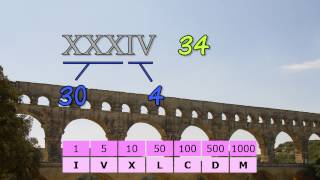 •
BC 0800? Roman Numerals
•
BC 0800? Roman Numerals
 ◌◌◌
dimension
◌◌◌
dimension

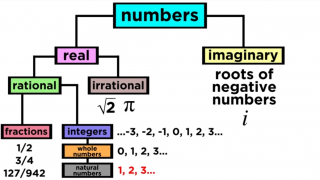 •
Types of Numbers
•
Types of Numbers