Whether differential or integral both concepts involve the idea that we can do something infinately many times and get a finite answer that is useful.
•
Calculus summary
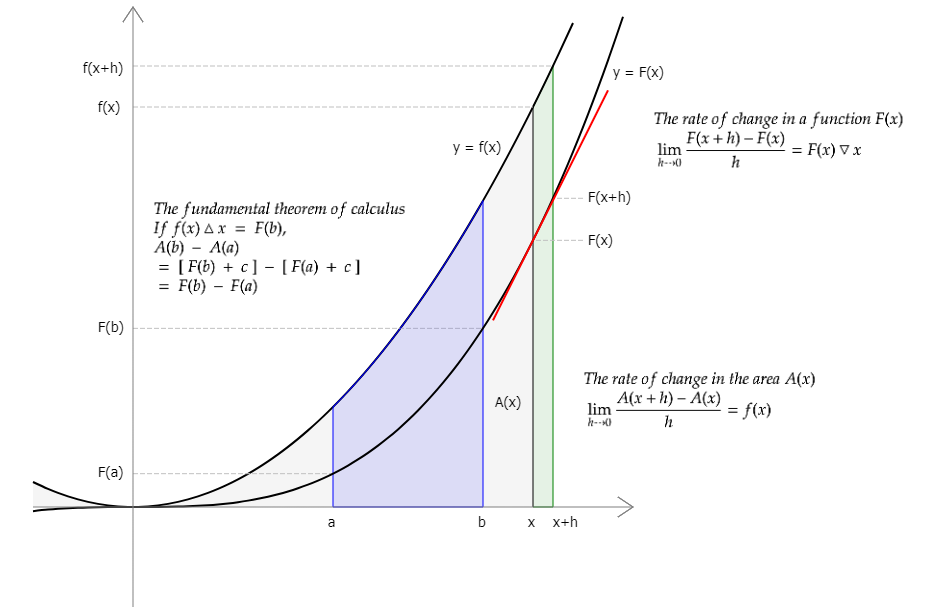
When x changes by h, the ratio of a change in F(x) to the change in x that caused it, is equal to (F(x+h)−F(x))/h. As h approaches 0, the limit of the ratio becomes a value. A function that maps x to this limit is called the derivative of F(x).
「(F(x+h)− ...
5028#3653
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
3653
 •
03 Rates of Change
•
03 Rates of Change
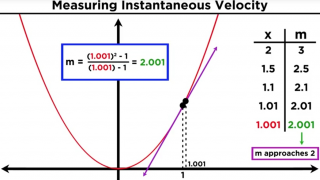
Galileo had already discovered some years prior that the distance traveled by a falling object is represented by a function of time. Newton wondered how one could calculate the velocity of the object at any particular instance during the fall.
5028#5034
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
5034
•
06 Power Rule proof
Definition of differentiation
(x˄n)▽x = 「((x+h)˄−x˄n)/h :h⨠0」
Binomial Expansion
(x+h)˄n
= 「n!/((n−k)!·k!)·x˄(n−k)·h˄k Σk=0,n」
(x+h)˄n − x˄n
= 「n!/((n−k)!·k!)·x˄(n−k)·h˄k Σk=1,n」
((x+h)˄n−x˄n) / h
= 「n!/((n−k)!·k!)·x˄(n−k)·h˄(k−1) Σk=1,n」
「((x+h)˄n−x˄ ...
5028#9687
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
9687
•
06 Product Rule proof
(f(x)·g(x))▽x
= 「(f(x+h)·g(x+h)−f(x)·g(x))/h :h⨠0」
= 「(f(x+h)·g(x+h)−f(x+h)·g(x)+f(x+h)·g(x)−f(x)·g(x))/h :h⨠0」
┅
−f(x+h)·g(x)+f(x+h)·g(x) inserted
┅
= 「(f(x+h)·g(x+h)−f(x+h)·g(x))/h :h⨠0」 + 「(f(x+h)·g(x)−f(x)·g(x))/h :h⨠0」
┅
split up into two limits
┅ ...
5028#9689
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
9689
•
06 Quotient Rule proof
(f(x)/g(x))▽x
= 「(f(x+h)/g(x+h)−f(x)/g(x))/h :h⨠0」
= 「(f(x+h)·g(x)−f(x)·g(x+h))/(g(x+h)·g(x))/h :h⨠0」 ➊
= 「(f(x+h)·g(x)−f(x)·g(x+h))/h/(g(x+h)·g(x)) :h⨠0」
= 「(f(x+h)·g(x)−f(x)·g(x+h))/h :h⨠0」
· 「1/(g(x+h)·g(x)) :h⨠0」
= 「((f(x+h)−f(x))·g(x)−f(x)·(g(x+h)−g( ...
5028#9692
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
9692
•
06 Taylor and Maclaurin Series
○ Power Series 「cₙ·x˄n Σn=0,∞」
○ Taylor Series
「f(x)▽ⁿx「a」/n!·(x−a)˄n Σn=0,∞」
○ Maclaurin Series
「f(x)▽ⁿx「0」/n!·x˄n Σn=0,∞」
┅
f(x)▽⁰x
= c₀·(x−a)˄0
+ c₁·(x−a)˄1
+ c₂·(x−a)˄2
+ c₃·(x−a)˄3 + ...
= 「cₙ·(x−a)˄n Σn=0,∞」
f(x)▽⁰x「a」 = c₀ = c₀·0!
c₀ = f(x)▽⁰x「a」/ ...
5028#9697
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
9697
•
08 Chain Rule proof
Definition of differentiation
f(g(x))▽x
= 「(f(g(x+h))−f(g(x)))/h :h⨠0」
= 「(f(g(x+h))−f(g(x)))/(g(x+h)−g(x))·(g(x+h)−g(x))/h :h⨠0」
= 「(f(g(x+h))−f(g(x)))/(g(x+h)−g(x)) :h⨠0」·「(g(x+h)−g(x))/h :h⨠0」
ᐥ
Let g(x+h)−g(x) = t, then 「t :h⨠0」 = 0 and g(x+h) = g(x) ...
5028#9693
SIBLINGS
CHILDREN
9693

-


 •
01 The Greeks, Newton and Leibniz
•
01 The Greeks, Newton and Leibniz
 •
01 The Greeks, Newton and Leibniz
•
01 The Greeks, Newton and Leibniz
 •
03 Rates of Change
•
03 Rates of Change
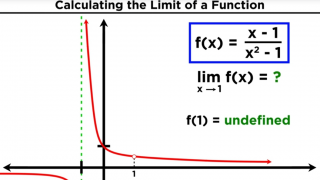 •
04 Limits and Limit Laws in Calculus
•
04 Limits and Limit Laws in Calculus
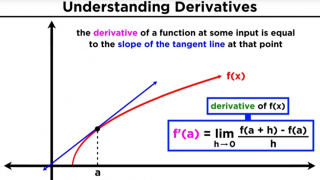 •
05 What is a Derivative?
•
05 What is a Derivative?
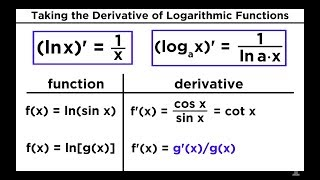 •
09 Derivatives of Logarithmic and Exponential Functions
•
09 Derivatives of Logarithmic and Exponential Functions
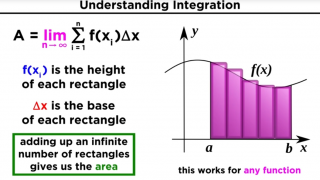 •
17 What is Integration?
•
17 What is Integration?
 •
18 The fundamental theorem of calculus
•
18 The fundamental theorem of calculus
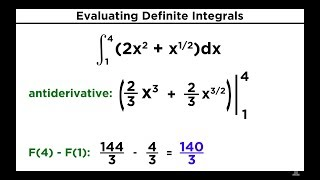 •
19 Properties of Integrals and Evaluating Definite Integrals
•
19 Properties of Integrals and Evaluating Definite Integrals
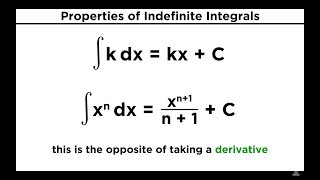 •
20 Evaluating Indefinite Integrals
•
20 Evaluating Indefinite Integrals
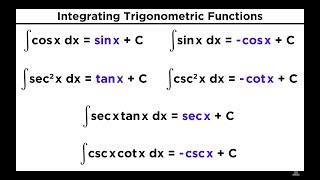 •
21 Evaluating Integrals With Trigonometric Functions
•
21 Evaluating Integrals With Trigonometric Functions
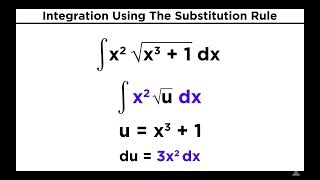 •
22 Integration Using The Substitution Rule
•
22 Integration Using The Substitution Rule
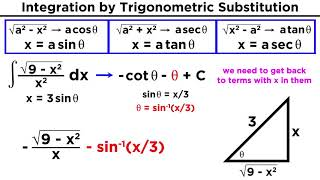 •
24 Integration by Trigonometric Substitution
•
24 Integration by Trigonometric Substitution
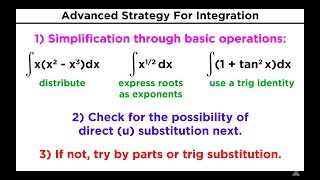 •
25 Advanced Strategy for Integration in Calculus
•
25 Advanced Strategy for Integration in Calculus
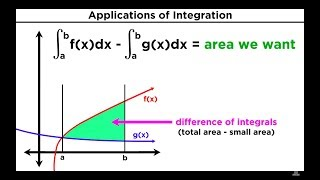 •
27 Finding the Area Between Two Curves by Integration
•
27 Finding the Area Between Two Curves by Integration
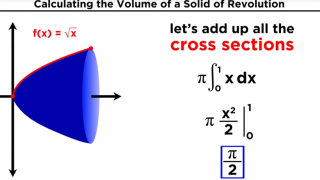 •
28 Calculating the Volume of a Solid of Revolution by Integration
•
28 Calculating the Volume of a Solid of Revolution by Integration
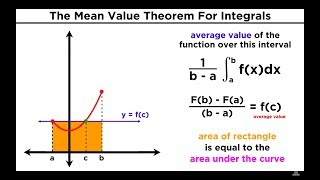 •
30 The Mean Value Theorem For Integrals: Average Value of a Function
•
30 The Mean Value Theorem For Integrals: Average Value of a Function